Extrinsic dark-pigmentation of the tooth enamel in pediatric dentistry
Keywords:
pigmentation, toothpaste, boy.Abstract
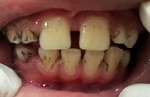
Dark enamel pigments are due to extrinsic staining and associated with aesthetic problems. The objective is to present two cases of children with black extrinsic pigmentation in the tooth enamel, with emphasis on the type of treatment and monitoring. This is a 5-year-old patient of who constantly used ferrous sulfate to treat anemia by iron deficiency, and another 12-year-old patient with type 1 diabetes and dermatomyositis. In the first case, we observed the presence of black extrinsic pigments in the primary teeth and the first permanent molars, especially in the lingual and vestibular part in the cervical region and middle third, together with incipient caries lesions on the occlusal surfaces of molars and active white spots on the first permanent molars. In the second case, there were strange black pigmentation in the cervical region of the smooth surfaces of the primary and permanent teeth. In the first case, the treatment performed was to remove black pigments and polishing the teeth by means of professional prophylaxis and using an abrasive toothpaste containing micro-granules of pumice. There was an improvement in the clinical aspect from the second session and the treatment ended at the fifth session. For the second case, we observed difficulty to remove the pigmented spots in the cervical region, together with the risk of bleeding gums. When the child needed prophylactic antibiotics, we opted for the daily control of the biofilm and it was not removed by professional cleaning, because the patient did not complain about the aesthetic impact. As conclusions, the extrinsic black pigments can be easily observed in children, and despite its aesthetic effect, it does damage oral health. It should be noted that it is unclear how their presence on the tooth surface reduces susceptibility to caries or tooth decay. In addition, the choice of treatment should always be based on the relation risk-benefit for the patient.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain all rights to their works, which they can reproduce and distribute as long as they cite the primary source of publication.
The Rev Cubana Estomatol is subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) and follows the publication model of SciELO Publishing Schema (SciELO PS) for publication in XML format.
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
- You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation.
- No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.

