Graftless maxillary sinus lift with simultaneous dental implant placement
Keywords:
dental implants, maxillary sinus lift, lateral window technique, transalveolar technique, blood clot.Abstract
Introduction: Maxillary sinus lift with simultaneous dental implantation without using bone substitutes, reapproaches the theory about the bone neoformation potential of the blood clot housed under the Schneider membrane, all by itself, thus excluding the need to use exogenous materials.
Objective: Discuss the effectiveness of graftless maxillary sinus lift with simultaneous dental implant placement through an evaluation of the amount of vertical bone gain.
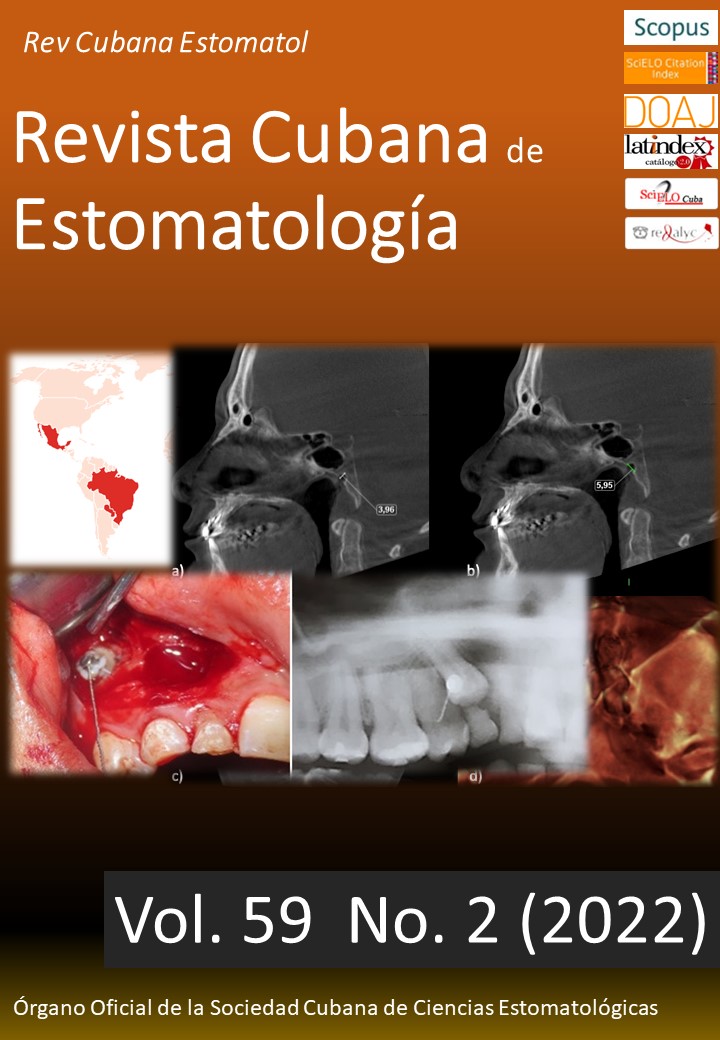
Case presentation: Case 1: Female 62-year-old patient undergoing graftless maxillary sinus lift with simultaneous dental implantation by lateral window technique due to a reduced bone height of 5.24 mm. After a 12-month tomographic follow-up period subsequent to prosthetic loading, a 10.2 mm vertical bone height was achieved, resulting in 4.96 mm vertical bone gain. Case 2: Female 48-year-old patient undergoing graftless maxillary sinus lift with simultaneous dental implantation by transalveolar technique using a piezoelectric generator due to a reduced bone height of 8.33 mm. After a 4-month radiographic follow-up period, before prosthetic loading, an 11.55 mm vertical bone height was achieved, resulting in 3.19 mm vertical bone gain.
Conclusions: According to these two case reports, graftless maxillary sinus lifting with simultaneous dental implantation is associated to reduced surgical morbidity, a lesser probability of infectious processes and lower surgical costs. It may therefore be considered to be a surgical alternative for implant placement in the posterior maxilla due to vertical bone deficiencies, regardless of the technique used (lateral or transalveolar).
Downloads
References
Boven GC, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A, Meijer HJ. Improving masticatory performance, bite force, nutritional state and patient's satisfaction with implant overdentures: a systematic review of the literature. J Oral Rehabil. 2015 Mar;42(3):220-33. doi: 10.1111/joor.12241.
Chiu T, Lee C, Bittner N, Prasad H, Tarnow DP, Schulze-Späte U. Histomorphometric Results of a Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Studying Maxillary Sinus Augmentation with Two Different Biomaterials and Simultaneous Implant Placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2018 Nov-Dec; 33(6):1320–30. doi: 10.11607/jomi.6778.
Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. Journal of Oral Surgery. 1980;38(8):613–616. PMID: 6993637
Summers RB. The osteotome technique: Part 3--Less invasive methods of elevating the sinus floor. Compendium. 1994 Jun;15(6):698, 700, 702-4 passim; quiz 710. PMID: 7994726
Franceschetti G, Farina R, Minenna L, Riccardi O, Stacchi C, Di Raimondo R, et al. The impact of graft remodeling on peri-implant bone support at implants placed concomitantly with transcrestal sinus floor elevation: A multicenter, retrospective case series. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2020 Feb;31(2):105-120. doi: 10.1111/clr.13541. Epub 2019 Sep 30.
Lundgren S, Andersson S, Gualini F, Sennerby L. Bone reformation with sinus membrane elevation: a new surgical technique for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2004;6(3):165-73. PMID: 15726851.
Pinchasov G, Juodzbalys G. Graft-free sinus augmentation procedure: a literature review. J Oral Maxillofac Res. 2014 Apr 1;5(1):e1. doi: 10.5037/jomr.2014.5101.
Falah M, Sohn DS, Srouji S. Graftless sinus augmentation with simultaneous dental implant placement: clinical results and biological perspectives. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016;45(9):1147-1153. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2016.05.006
Kuhl S, Payer M, Kirmeier R, Wildburger A, Acham S, Jakse N. The influence of particulated autogenous bone on the early volume stability of maxillary sinus grafts with biphasic calcium phosphate: a randomized clinical trial. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2015; 17:173-178. doi: 10.1111/cid.12086
Rodriguez AE, Nowzari H. The long-term risks and complications of bovine derived xenografts: a case series J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2019 Sep-Oct;23(5):487-492. doi: 10.4103/jisp.jisp_656_18.
Duan DH, Fu JH, Qi W, Du Y, Pan J, Wang HL. Graft free maxillary sinus floor elevation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Periodontol. 2017 Jun;88(6):550-564. doi: 10.1902/jop.2017.160665.
Silva LD, de Lima VN, Faverani LP, de Mendonça MR, Okamoto R, Pellizzer EP. Maxillary sinus lift surgery-with or without graft material? A systematic review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2016 Dec;45(12):1570-1576. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2016.09.023.
De Oliveira GR, Olate S, Cavalieri Pereira L, Pozzer L, Asprino L, de Moraes M, et al. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation using blood without graft material. Preliminary results in 10 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;71: 1670–1675. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2013.05.025
Parra M, Atala-Acevedo C, Fariña R, Haidar ZS, Zaror C, Olate S. Graftless maxillary sinus Lift Using Lateral Window Approach: A Systematic Review. Implant Dent. 2018 Feb;27(1):111-118. doi: 10.1097/ID.0000000000000695.
Tilaveridis I, Lazaridou M, Zouloumis L, Dimitrakopoulos I, Tilaveridis V, Tilaveridou S. The use of mineralized bone allograft as a single grafting material in maxillary sinus lifting with severely atrophied alveolar ridge (1-3 mm) and immediately inserted dental implants. A 3- up to 8-year retrospective study. Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2018; 22(3):267–73. DOI: 10.1007/s10006-018-0698-6
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Authors retain all rights to their works, which they can reproduce and distribute as long as they cite the primary source of publication.
The Rev Cubana Estomatol is subject to the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) and follows the publication model of SciELO Publishing Schema (SciELO PS) for publication in XML format.
You are free to:
- Share — copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format.
- Adapt — remix, transform, and build upon the material.
The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms.
Under the following terms:
Attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- NonCommercial — You may not use the material for commercial purposes.
No additional restrictions — You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits.
Notices:
- You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation.
- No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material.