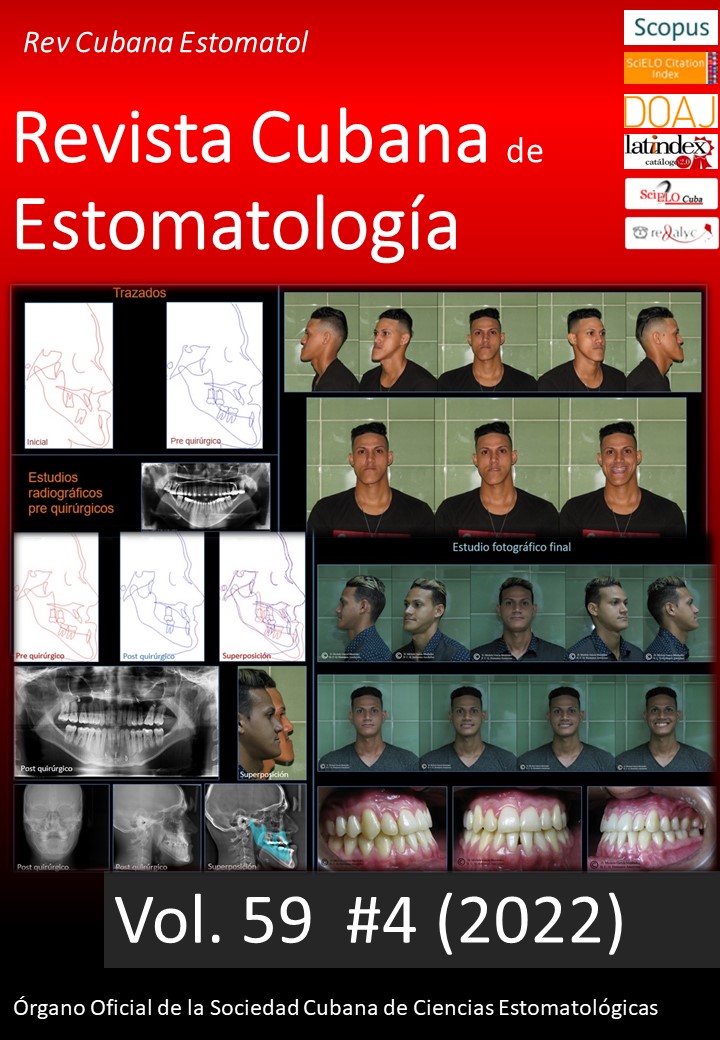
Tratamiento integral de la clase III esquelética severa, mordida abierta y asimetría facial
Palabras clave:
Cirugía ortognática, ortodoncia, procedimientos quirúrgicos ortognáticos, cirugía máxilo mandibularResumen
Introducción: La cirugía ortognática está especialmente indicada en casos complejos, donde los procedimientos conservadores fracasan o son insuficientes. El diagnóstico, planificación y tratamiento deben estar a cargo de un equipo multidisciplinario que trabaje en estrecha relación.
Objetivo: Reportar el trabajo multidisciplinario en el tratamiento ortodóncico quirúrgico de una desarmonía dentomaxilofacial compleja.
Presentación de caso: Paciente masculino, 19 años de edad, mestizo, clase III esquelética grave, hiperdivergente con mordida abierta y asimetría del tercio inferior, que recibió tratamiento prequirúrgico descompensador de ortodoncia. Se realizó cirugía ortognática bimaxilar con genioplastia de ascenso.
Conclusiones: El tratamiento de las desarmonías dentomaxilofaciales es complejo y necesita la concurrencia de varias especialidades. Para la resolución del presente caso fue necesario el trabajo coordinado y simultáneo de especialistas de ortodoncia, prótesis dental, cirugía maxilofacial, periodoncia, psicología y otorrinolaringología. Se alcanzaron resultados estéticos y funcionales acorde a los objetivos del tratamiento propuestos y hubo estabilidad un año después de la cirugía.
Descargas
Citas
Thiesen G, Gribel BF, Freitas MPM, Oliver DR, Kim KB. Mandibular asymmetries and associated factors in orthodontic and orthognathic surgery patients. The Angle Orthodontist; 2018 [acceso 19/07/2020];88(5):[aprox. 7 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8183131/
Thiesen G, Gribel BF, Freitas MPM. Facial asymmetry: a current review. Dental press journal of orthodontics; 2015 [acceso 22/07/2020]; 20(6):[aprox. 16 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4686752/
Srivastava D, Singh H, Mishra S, Sharma P, Kapoor P, Chandra L. Facial asymmetry revisited: Part I- diagnosis and treatment planning. Journal of oral biology and craniofacial research; 2018 [acceso 19/07/2020];8(1):[aprox 8 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5854562/
Denadai R, Chou P-Y, Su Y-Y, Lin H-H, Ho C-T, Lo L-J. The Impacts of Orthognathic Surgery on the Facial Appearance and Age Perception of Patients Presenting Skeletal Class III Deformity: An Outcome Study Using the FACE-Q Report and Surgical Professional–Based Panel Assessment. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery; 2020 [acceso 19/07/2020]; 145(4):[aprox 12 p.]. Disponible en: https://journals.lww.com/plasreconsurg/Fulltext/2020/04000/The_Impacts_of_Orthognathic_Surgery_on_the_Facial.38.aspx.
Soto Fernández A. Cirugía ortognática básica. La Habana: Editorial Capitán San Luis; 2014.
Gregoret J, Tuber E, Escobar P LH, Matos da Fonseca A. Ortodoncia y cirugía ortognática. Barcelona: ESPAXS,SA; 1997.
Hospital Clínico Quirúrgico Hermanos Ameijeiras. Manual de prácticas médicas. 6 ed. La Habana: CEDISAP; 2018.
Johnston C, Burden D, Kennedy D, Harradine N, Stevenson M. Class III surgical-orthodontic treatment: A cephalometric study. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics; 2006 [acceso 19/07/2020]; 130(3):[aprox 10 p.]. Disponible en: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0889540606005798
Kim KA, Lee JW, Park JH, Kim BH, Ahn HW, Kim SJ. Targeted presurgical decompensation in patients with yaw-dependent facial asymmetry. Korean J Orthod; 2017 [acceso 19/07/2020]; 47(3):[aprox. 12 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5432441/
Oh SH, Nahm K-Y, Kim S-H, Nelson G. Alveolar bone thickness and fenestration of incisors in untreated Korean patients with skeletal class III malocclusion: A retrospective 3-dimensional cone-beam computed tomography study. Imaging Sci Dent [Internet]. 2020 [acceso 19/07/2020]; 50(1):[aprox. 6 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7078404/.
Park J-H, Hong J-Y, Ahn H-W, Kim S-J. Correlation between periodontal soft tissue and hard tissue surrounding incisors in skeletal Class III patients. The Angle Orthodontist; 2018 [acceso 19/07/2020];88(1):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://meridian.allenpress.com/angle-orthodontist/article/88/1/91/57503/Correlation-between-periodontal-soft-tissue-and
Matsumoto K, Sherrill-Mix S, Boucher N, Tanna N. A cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation of alveolar bone dimensional changes and the periodontal limits of mandibular incisor advancement in skeletal Class II patients. The Angle Orthodontist; 2020 [acceso 19/07/2020]; 90(3):[aprox. 9 p.]. Disponible en: https://meridian.allenpress.com/angle-orthodontist/article/90/3/330/430032/A-cone-beam-computed-tomographic-evaluation-of
Damstra J, Fourie Z, De Wit M, Ren Y. A three-dimensional comparison of a morphometric and conventional cephalometric midsagittal planes for craniofacial asymmetry. Clinical oral investigations; 2012 [acceso 19/07/2020];16(1):[aprox. 10 p.]. Disponible en: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3259389/
Proffit WR. Ortodoncia teoría y práctica. 2 ed. Madrid: Mosby; 1994.
Castiñeira López D, Machado Martínez M. La inclusión del tema envejecimiento facial en el proceso de enseñanza-aprendizaje de la Ortodoncia. Gaceta Médica Espirituana; 2017 [acceso 29/07/2020]; 19(1):[aprox 5 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1608-89212017000100004&nrm=iso
Blanco Mederos FM, Blanco Ramos K, Pichardo Valiente MA, Soto Caballero D, Garcia Pulido E, Rodríguez Sarduy R. Comportamiento de la oclusión dentaria en pacientes operados de cirugía ortognática. Revista Médica Electrónica; 2017 [acceso 29/07/2020];39(1):[aprox 12 p.]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1684-18242017000200006&nrm=iso
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Los autores conservan todos los derechos sobre sus obras, las cuales pueden reproducir y distribuir siempre y cuando citen la fuente primaria de publicación.
La Revista Cubana de Estomatología se encuentra sujeta bajo la Licencia Creative Commons Atribución-No Comercial 4.0 Internacional (CC BY-NC 4.0) y sigue el modelo de publicación de SciELO Publishing Schema (SciELO PS) para la publicación en formato XML.
Usted es libre de:
- Compartir — copiar y redistribuir el material en cualquier medio o formato
- Adaptar — remezclar, transformar y construir a partir del material.
La licencia no puede revocar estas libertades en tanto usted siga los términos de la licencia
Bajo los siguientes términos:
- Atribución — Usted debe dar crédito de manera adecuada, brindar un enlace a la licencia, e indicar si se han realizado cambios. Puede hacerlo en cualquier forma razonable, pero no de forma tal que sugiera que usted o su uso tienen el apoyo de la licenciante.
- No Comercial — Usted no puede hacer uso del material con propósitos comerciales.
- No hay restricciones adicionales — No puede aplicar términos legales ni medidas tecnológicas que restrinjan legalmente a otras a hacer cualquier uso permitido por la licencia.
Avisos:
- No tiene que cumplir con la licencia para elementos del material en el dominio público o cuando su uso esté permitido por una excepción o limitación aplicable.
- No se dan garantías. La licencia podría no darle todos los permisos que necesita para el uso que tenga previsto. Por ejemplo, otros derechos como publicidad, privacidad, o derechos morales pueden limitar la forma en que utilice el material.